Introduction
SAP S/4HANA Cloud is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) product, which means that the software is licensed on a subscription basis and is accessed via the Internet. SAP takes care of many tasks for you, such as installation and upgrades, so that you can concentrate more on your business. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the key differentiators, features, and factors to consider when making the pivotal decision between SAP’s public and private cloud offerings. Join us as we explore the path to a more streamlined, secure, and intelligent enterprise platform.
SAP S/4 Hana Public Cloud
SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition is a cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) software suite that is designed to help businesses of all sizes run more efficiently. It is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) product, which means that it is hosted and managed by SAP. This means that businesses do not need to install or maintain any hardware or software, and they can access the software from anywhere with an internet connection.
SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition is a comprehensive ERP suite that includes modules for all core business processes, such as finance, accounting, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management (CRM). It is also highly scalable, making it usable by businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises.
SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition is a popular choice for businesses that are looking for a modern, cloud-based ERP solution that can help them improve their efficiency and agility. It is a cost-effective solution that is easy to implement and use. A small to medium-sized business that needs a scalable and affordable ERP solution without the need for a lot of customization.
Here are some of the benefits of using SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition:
- Reduced IT costs: Businesses do not need to invest in hardware or software, and they can save on IT maintenance costs.
- Improved efficiency: SAP S/4HANA Cloud can help businesses automate many of their manual processes, which can free up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Increased agility: SAP S/4HANA Cloud is a cloud-based solution, so businesses can easily add new users and functionality as their needs change.
- Scalability: SAP S/4HANA Cloud can be used by businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises.
SAP S/4 Hana Private Cloud
In the context of SAP, a private cloud refers to a dedicated cloud computing environment exclusively used by a single organization. This implies that the organization exercises full control over the infrastructure, whether it is hosted on-premises within their own data center or with a dedicated cloud provider. In a private cloud, the organization has the ability to implement its own security measures and compliance policies, providing a higher level of data protection and regulatory adherence.
Scalability is available in a private cloud, but it may require more effort to expand resources compared to a public cloud. However, the performance can be optimized to meet specific requirements, making it suitable for applications with demanding performance needs. While setting up a private cloud involves higher upfront capital expenditures for infrastructure, it can be a cost-effective solution for organizations with predictable workloads or budget constraints in the long run
Private clouds also offer greater customization options, allowing organizations to tailor the infrastructure to meet their specific needs. Additionally, integration with other systems tends to be easier in a private cloud environment. Overall, a private cloud in SAP provides a secure, controlled, and customizable computing environment for organizations with specific requirements or regulatory constraints.
Difference between Public vs Private Cloud Features
| Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
| Control of Infrastructure | Less control, hosted by cloud service provider (SAP) | More control, hosted on-premises or with a dedicated cloud provider (Third Parties) |
| Security and Compliance | Relies on cloud service provider’s security measures and compliance policies | Greater control over implementing own security measures and compliance policies |
| Scalability | Easily scalable with minimal effort to expand resources | Scalable, but may require more effort to expand resources |
| Performance Optimization | Standardized performance based on provider’s offerings | Can be optimized based on specific requirements |
| Capital Expenditures | Lower upfront capital expenditures | Higher upfront capital expenditures, but can be cost-effective for predictable workloads or budget constraints |
| Customization and Integration | Limited customization options, standardized infrastructure | Offers greater customization options, allowing tailoring to specific needs and easier integration with other systems |
Comparing Public vs Private Cloud
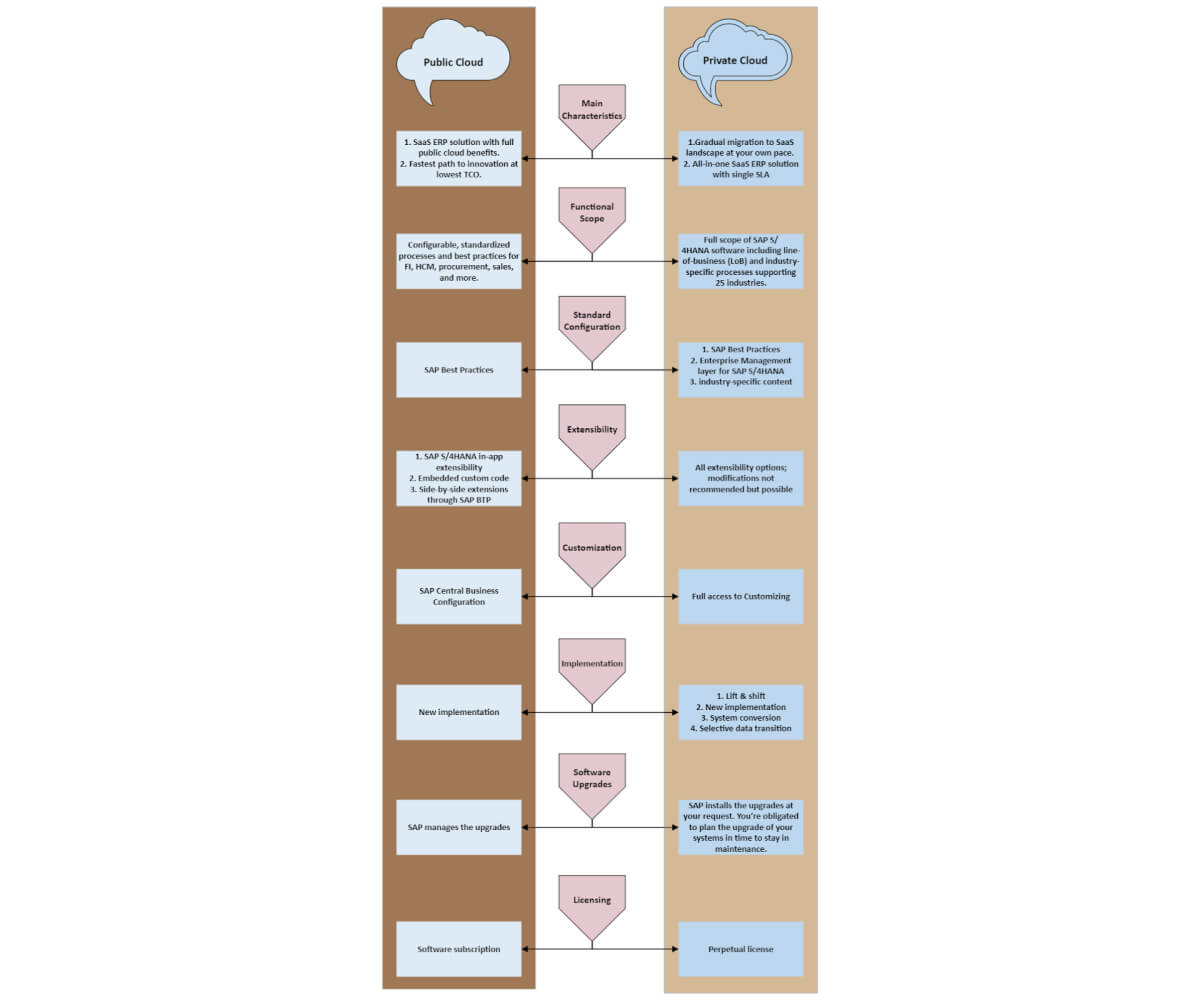
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Public vs Private Cloud for Your Organization
Data Sensitivity and Compliance:
If your organization deals with highly sensitive data or operates in a strict compliance industry, a private cloud offers greater control. It provides enhanced security measures for data protection.
Customization Needs:
Resource Scalability:
If your organization anticipates the need for rapid resource scaling, a public cloud may offer more immediate and easily scalable resources. However, a private cloud can also accommodate scalability with some effort.
Performance Demands:
For applications with demanding performance requirements, a private cloud allows for fine-tuning and optimization to meet those needs effectively.
Cost Considerations:
A private cloud may require higher upfront capital expenditures for infrastructure. However, it can be cost-effective in the long term for organizations with predictable workloads or budget constraints.
Integration with Existing Systems:
If your organization relies heavily on existing systems and requires seamless integration, a private cloud environment may offer easier integration. This is compared to a public cloud.
Security and Control:
Predictable Workloads:
Regulatory Adherence:
Industries with stringent regulatory requirements may benefit from a private cloud. It allows for more precise adherence to specific regulations and compliance standards.
Multi-Tenancy Concerns:
A private cloud eliminates concerns about sharing resources with other organizations in a multi-tenant environment. It’s ideal for those prioritizing data security and exclusivity.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital transformation, choosing the right cloud strategy is paramount. Organizations strive for efficiency, security, and compliance. The decision between SAP’s S/4HANA Public Cloud and Private Cloud hinges on a myriad of factors. These range from data sensitivity to customization needs and regulatory adherence. Understanding the nuances and advantages of each option empowers businesses to make informed choices that align with their specific requirements.
Ultimately, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The optimal choice lies in a careful consideration of your organization’s unique circumstances and long-term objectives. Whether you prioritize immediate scalability, robust security measures, or a tailored infrastructure. SAP’s cloud offerings pave the way for a more streamlined, secure, and intelligent enterprise platform. Embracing the power of the cloud ensures that your organization remains agile and poised to thrive in the digital era. Public vs Private Cloud Public vs Private Cloud Public vs Private Cloud Public vs Private Cloud
To read more of our blogs you can surely click here.
check out other video blogs
Disclaimer: All the opinions are solely for information purposes and the author doesn’t recommend or reject any tools. You should do it after your own due diligence.

